Deep Vein Thrombosis
What is a DVT?
A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in the deep veins of the legs, pelvis, or arms. Blood flows through the vessels like water in a pipe. When a blood vessel is narrowed, damaged, or scarred, a blood clot can form. They can also form in people who do not move enough or who have blood clot disorders.
Larger clots can cause severe pain and swelling. If a clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, it is a life-threatening condition called a pulmonary embolism (PE). Over time, DVTs can also damage the veins. This can cause limb swelling, ulcers, and pain called post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS).
How is DVT treated?
Most DVTs can be treated with blood thinners to prevent new clots from forming while the body clears the DVT over time. People with severe symptoms or a high risk of developing a PE or PTS may benefit from a minimally invasive procedure to dissolve the blood clot (called thrombolysis) or remove it (called thrombectomy).
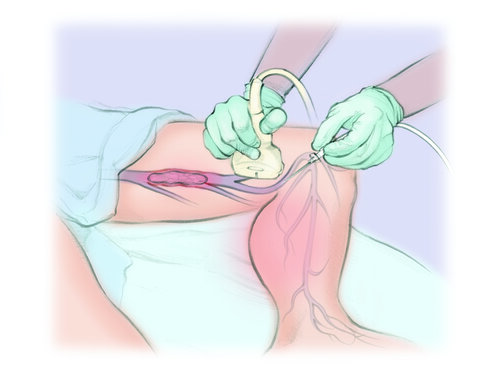
The clinician starts by cleaning and numbing the skin over a vein in the neck, top of the thigh, or back of the knee or ankle. Then they thread a tiny tube into the vein using moving x-rays to guide it to the clot.
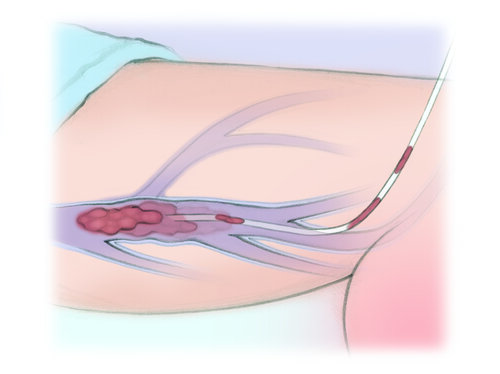
Sometimes they can suck out the clot or break it up (thrombectomy). Other times, they dissolve the clot by slowly dripping clot-busting medicine through a tiny soaker hose-like tube (thrombolysis). This can take hours to days, and you have to be watched closely in the intensive care unit (ICU). You may not be allowed to get out of bed or eat during this time. You may also have another procedure to make sure the clot has improved. The tube is then removed and a bandage is placed over the wound.
What are the risks?
DVT Thrombectomy / Thrombolysis are generally safe procedures when done by a specialist.
1 in 2 people will still develop PTS after treatment for DVT.
6 in 100 people will have bleeding over the next 2 years. Since the treatment of DVT relies on blood-thinning medicines, bleeding is the main risk. The risk of serious bleeding in the brain or other parts of the body depends on your other health problems.
Less than 5 in 100 people experience clot breaking off and traveling to the lungs
Less than 2 in 100 people develop damage to the blood vessels, experience bleeding, develop infection
What are the alternatives?
Your options will depend upon your specific health issues and preferences. Your clinician will be able to help you explore your options, including a combination of the treatments below.
Alternative 1 No treatment. This avoids any risks or discomfort of treatment but has the highest risk of the clot not going away. If the clot stays, the symptoms will likely not improve. Up to 1 in 2 of untreated people will develop PE because the clot travels to the lungs – this can be life-threatening.
Alternative 2 Most DVTs are treated with blood thinners. This prevents the clot from growing while the body breaks down the clot. This option avoids a procedure and has less bleeding risk (4 in 100 people have major bleeding) but is less effective for large or high-risk clots. With this treatment, 2-5 in 100 people have clot travel to the lungs (PE).
Alternative 3 Clot-busting medicine (”tPA”) through an IV plus blood thinners. This option has a higher bleeding risk (9 in 100 people) since the medicine is not targeted to the clot.
Alternative 4 Surgery to remove the clot. This is avoided because it has a much higher risk of complications and often does not work for very long.
What is a PE?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot in the blood vessels going to the lungs. A PE prevents blood from reaching the lungs. Smaller clots can cause shortness of breath and chest pain. Larger clots can cause heart failure and even death.
PEs come from blood clots that form in the deep veins of the limbs or pelvis. This type of clot is called a deep vein thrombosis, or DVT. These clots can get carried by the blood to the lungs, where they become a PE.
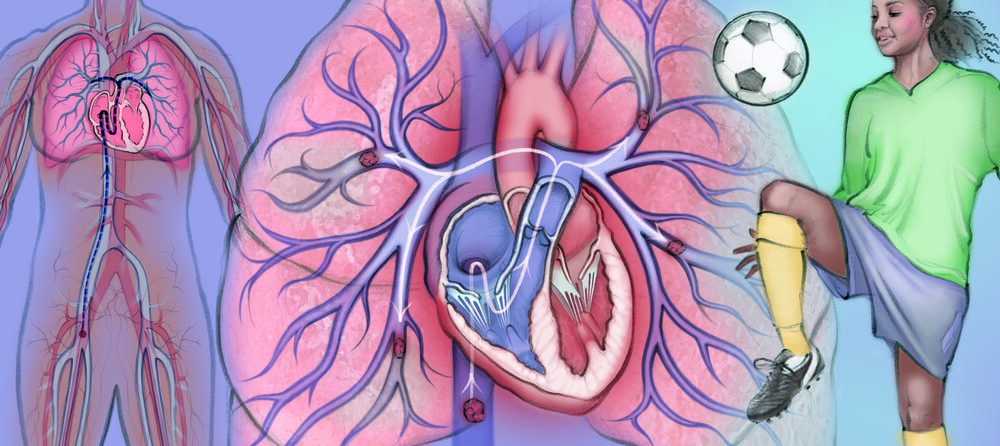
How is PE treated?
Most PEs and DVTs can be treated with blood thinners to prevent new clots from forming while the body dissolves the PE on its own over time. However, this may not be fast enough for people with severe symptoms from larger DVTs or a high risk of developing a PE or PTS. These people may benefit from a minimally invasive procedure where the blood clot is dissolved (called thrombolysis) or removed (called thrombectomy).
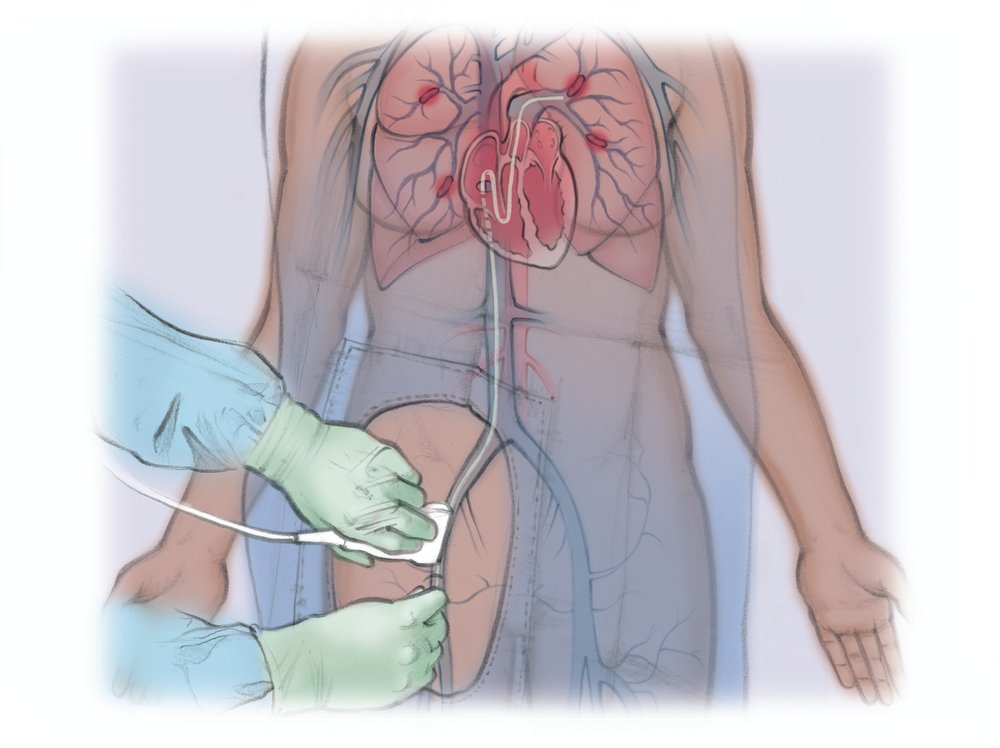
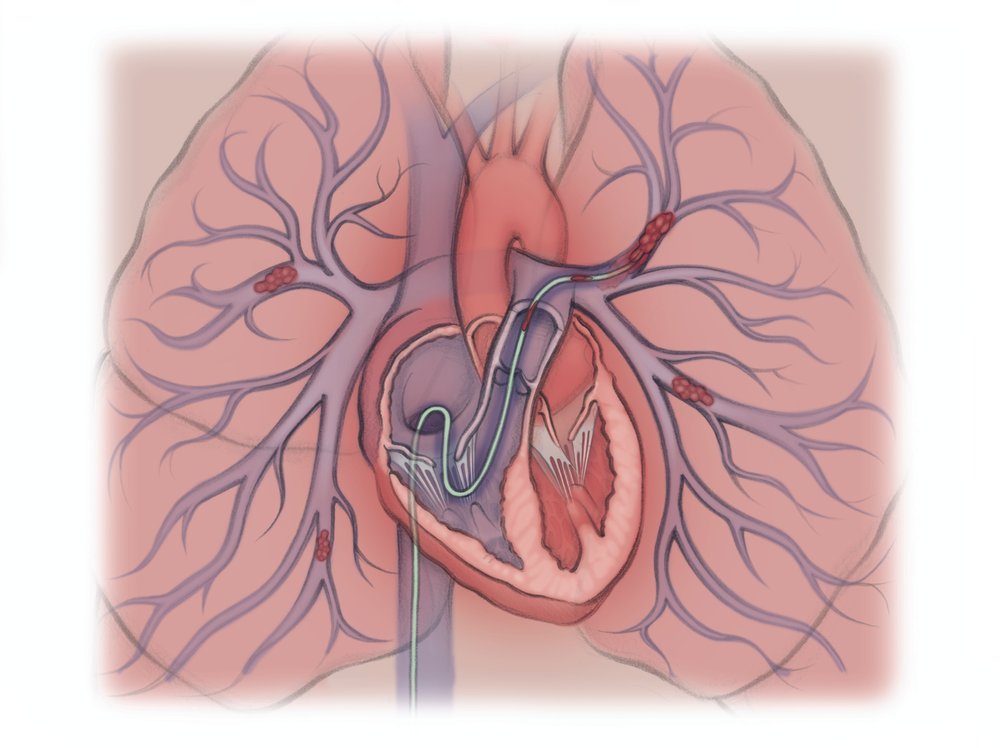
The clinician starts by cleaning and numbing the skin of the neck or top of the thigh. Then they thread a tiny tube into a large vein. They use moving x-rays to guide the tube through the veins to where the clot is in the lungs.
Sometimes they can suck out the clot or break it up (thrombectomy). Other times, the clinician leaves a tiny soaker hose-like tube that slowly delivers clot-busting medicine to dissolve the clot (thrombolysis).
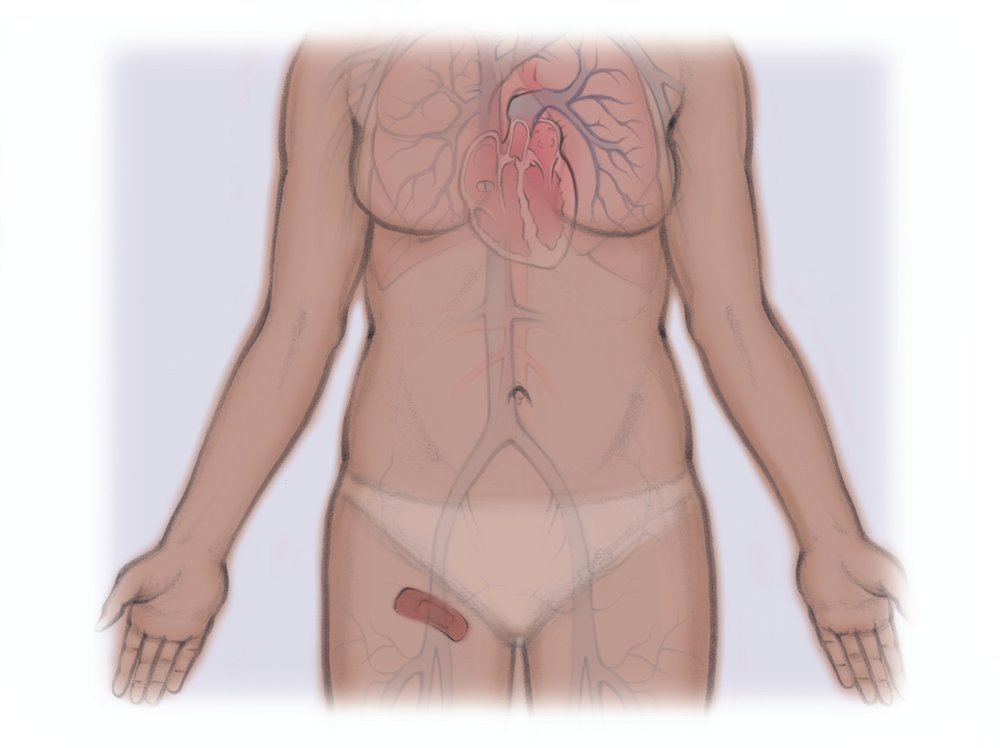
If the tube is left in place to dissolve the clot, you have to be watched closely in the intensive care unit (ICU). You may not be allowed to get out of bed or eat during this time. You may also be brought back for an additional procedure to make sure the clot has dissolved. The tube is then removed and a bandage is placed over the wound.
What are the risks?
PE Thrombectomy / Thrombolysis are generally safe procedures when done by a specialist.
Since the treatment of PEs relies on blood-thinning and sometimes clot-busting medicines, bleeding is the main risk. Different people have different bleeding risks based on past health issues, recent surgery, or trauma.
Less than 1 in 100 people with low bleeding risk develop significant bleeding.
Other risks include infection, damage to blood vessels, and abnormal heart beats.
What are the alternatives?
Your options will depend upon your specific health condition and your preferences. Your clinician will discuss these with you.
Alternative 1 Most PEs can be treated with blood thinners to prevent new clots from forming while the body dissolves the PE on its own. This has a low bleeding risk (3 in 100 people) but may not work fast enough if clots are large and life-threatening.
Alternative 2 Clot-busting medicine (“tPA”) through an IV plus blood thinners. This option has a higher bleeding risk (9 in 100 people) since the medicine is not targeted to the clot.
Alternative 3 Surgery to remove the clots. This is rarely done because many people with large clots are too sick to survive the surgery.